Snapchat Is Putting a 5GB Cap on Free Memories Storage.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Samsung Unveils 'Moohan' XR Headset, Pushing Android into Mixed Reality.
An XR Headset Designed for the Future of AI.
Targeting the Prosumer Market.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Qualcomm and Google Join Forces to Bring a Full Android Experience to PCs.
In a significant move that could blur the lines between mobile and desktop computing, Google and Qualcomm are officially collaborating on a project to bring a full, uncompromised version of Android to PCs. The announcement, made at Qualcomm's Snapdragon Summit, signals a major push to create a new category of devices powered by a unified operating system foundation.
For years, Android's presence on desktops has been limited to emulators and half-baked third-party solutions. Now, Google's Senior Vice President of Devices and Services, Rick Osterloh, and Qualcomm CEO Cristiano Amon have confirmed that they are building a "common technical foundation" that will leverage the best of both Android and ChromeOS.
A New Vision for a Unified Platform.
This initiative builds upon Google's prior announcement to merge the core of ChromeOS with Android, but with a critical difference: the platform will be designed from the ground up to support a desktop form factor. This means native support for mouse and keyboard input, large screens, and a multitasking experience that mirrors traditional PC use, while still retaining the vast Android app ecosystem.
During the summit, Amon expressed his excitement, stating he had seen the project and called it "incredible." He believes it "delivers on the vision of convergence in mobile and PC." This is a strong vote of confidence, especially considering the project is expected to be powered by Qualcomm's high-performance Snapdragon X series chipsets, including the Snapdragon X Elite.
The Race to AI-Powered PCs.
This new Android desktop venture is perfectly timed to ride the wave of AI PCs. The new platform will be deeply integrated with Google's Gemini models and its full AI stack, allowing for on-device, generative AI features that run with incredible speed and efficiency. This could give Qualcomm and Google a compelling competitive edge against traditional x86 laptops, which are still playing catch-up in the on-device AI space.
While the concept of Android on a PC isn't new, this official collaboration between two tech giants changes everything. The project's success will hinge on performance, developer support, and the ability to convince users that a full-featured Android PC can truly replace a traditional Windows or macOS machine. With no official timeline announced, the tech world will be watching closely to see if this new venture can succeed where others have failed.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Google Photos 'Help me edit' AI Feature Expands to All Android Users.
Key Features and How It Works.
- "Remove the glare, brighten the photo, and add clouds to the sky."
- "Make the colors pop and sharpen the subject."
- "Restore the photo" for old, faded, or damaged images.
Availability and Requirements.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Unveiling Android 16 QPR2 Beta 2: A Deep Dive into What's New and What's Next.
The latest iteration of Android, specifically Android 16 QPR2 Beta 2, has just dropped, bringing with it a fascinating array of new features and under-the-hood enhancements. While quarterly platform releases (QPRs) often focus on stability and minor tweaks, this beta release is particularly rich, offering a glimpse into Google's strategic direction for security, privacy, user customization, and developer tools.
From robust new protections for sensitive data to a deeper integration with health and fitness, and even more expressive personalization options, this update touches on nearly every facet of the Android experience.
Join us as we explore each significant change in detail, dissecting what these updates mean for users, developers, and the future of the Android ecosystem.
1. Testing developer verification.
Based on the Android 16 QPR2 Beta 2 release information, developer verification is a new security requirement designed to make the Android ecosystem safer for users. It's a key part of Google's effort to combat the spread of malware and scams from malicious apps.
Starting in September 2026, Android will begin requiring that apps be registered by verified developers to be installed on certified Android devices in certain regions. This change links real-world individuals and organizations to their applications, making it more difficult for "bad actors" to operate anonymously and repeatedly.
For developers, this beta release includes new APIs that support the verification process during app installation. It also introduces a new adb command that allows developers to simulate successful and unsuccessful verification outcomes for testing purposes. This gives them the tools to prepare for the upcoming enforcement of this security measure, ensuring a smooth transition for their apps.
2. SMS OTP Protection.
A new layer of security is being added to the Android ecosystem to protect users from a common threat. The latest beta introduces a powerful SMS OTP Protection feature, which is designed to combat the hijacking of one-time passwords by malicious apps.
This new security measure works by strategically delaying the delivery of certain SMS messages that contain an OTP. For most apps, the message will be held back for up to three hours. This deliberate hold makes it virtually impossible for malware to intercept and use the OTP in real time, giving you a crucial window to spot and stop suspicious activity.
Crucially, this protection is designed not to disrupt your daily usage. Core system apps like your default SMS app, phone dialer, and Google Assistant are exempt from the delay. Similarly, apps that use Google’s official SMS Retriever API will continue to receive OTPs instantly, maintaining a seamless and secure experience for services that are built to be compliant.
3. New App Icon Shapes Arrive in Beta.
Beyond its security and privacy updates, Android 16 QPR2 Beta 2 is also empowering users with a new level of home screen customization. The latest beta introduces native support for custom app icon shapes, a highly anticipated feature that allows users to overhaul the look of their app icons without the need for a third-party launcher.
This new tool, found under Settings > Wallpaper & style > Icons, gives users five different shapes to choose from: the classic Circle and Square, as well as more unique shapes like a "cookie" and an arch. The selected shape is applied universally to all app icons and even folder previews, creating a cohesive and visually refreshed home screen experience.
This addition aligns with Google's ongoing effort to make Android more customizable and personal. By giving users more control over their device's aesthetics, Google is not only improving the user experience but also bringing a feature that has long been available on other platforms directly into the core Android OS.
4. The New Era of Garbage Collection.
Among the most significant under-the-hood improvements in the Android 16 QPR2 Beta 2 is a complete overhaul of the Android Runtime (ART) garbage collector. This update brings a Generational Concurrent Mark-Compact (CMC) Garbage Collector to the platform, a technical change that translates directly into a more fluid and efficient user experience.
Previously, garbage collection could cause noticeable stutters or "jank" as the system paused to clean up unused data. This new approach is much smarter. It works in the background and focuses its efforts on newly allocated objects, which are more likely to be discarded anyway. This reduces the workload on the phone's CPU, minimizing interruptions and making the entire interface, from scrolling through apps to navigating the home screen, feel smoother and more responsive. The result is not just a better feel, but also improved battery efficiency, as the processor spends less energy on maintenance.
This change is a prime example of how Google is focusing on foundational performance. By making the core of the operating system more intelligent and efficient, they are paving the way for a faster, more reliable Android experience for everyone, regardless of the app they are using.
5. Health and Fitness Just Got Smarter with Health Connect.
In a move that could transform how Android users manage their health, the latest beta introduces a significant upgrade to Health Connect. Previously, the platform acted as a simple data hub, relying on third-party apps and wearables to provide information. Now, Health Connect is evolving into a proactive fitness tool with native step tracking.
This means your Android phone can now automatically count your steps using its built-in sensors, eliminating the need to download a separate step-counting app. This data is then made available to any app with the appropriate permissions, creating a more cohesive and accurate fitness experience. In addition, the update expands the data types for exercises, allowing apps to record more detailed metrics such as weight, set index, and Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) during a workout.
By building these foundational features directly into the OS, Google is making fitness tracking more accessible and efficient for everyone. It simplifies the user experience, reduces battery drain, and provides developers with a reliable, system-level source of data to build more powerful and insightful health apps.
More Than Just Features: The Under-the-Hood Innovations.
While the user-facing features of Android 16 QPR2 Beta 2 are significant, the update also brings a host of critical, yet less visible, changes that pave the way for a more innovative and consistent Android platform. One of the most important of these is the introduction of a minor SDK version. This is a major change for developers, as it allows Google to roll out new APIs and capabilities more rapidly throughout the year, without being tied to a major annual platform release.
Beyond the SDK version bump, the beta is packed with other refinements that promise a better user experience. Developers can now take advantage of a new Expanded Dark Theme option, which intelligently inverts the UI of apps that lack native dark theme support, providing a consistent look system-wide.
The update also includes a new PDF document editing API, which significantly expands the platform's native support for annotating and editing PDF files. For developers, this means the foundation is in place to build more powerful and integrated PDF experiences directly into their apps. Finally, a Display Topology API is being introduced to support advanced multi-display setups, giving apps the information they need to create fluid, multi-screen experiences on devices like foldables and tablets.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Android 16 Update Turns Your App Icons into Cookies.
A Deeper Dive into Icon Shapes.
- Circle (the default)
- Square
- Four-sided "cookie"
- Seven-sided "cookie"
- Arch
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5 Is Here, and It’s a Beast.
Qualcomm is finally pulling back the curtain on its next big thing. At its annual Snapdragon Summit, the company confirmed the name of its next flagship mobile processor: the Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5. This isn't just a new chip; it's a new era of naming conventions that's designed to bring a little more clarity to the top of its lineup.
Forget the confusing, seemingly random name changes. The new "Gen 5" name is a direct continuation of the Snapdragon 8-series line, following the original Gen 1 through Gen 3, and treating last year’s Snapdragon 8 Elite as the de facto "Gen 4." Now that we’ve got that straight, let’s get to the good stuff.
The Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5 is expected to be a performance powerhouse. It’s built on Qualcomm’s custom Oryon CPU architecture that blew us away last time, and now it’s rumored to be running with a crazy-fast 4.61 GHz clock speed on its main cores. On the graphics side, we’re looking at the all-new Adreno 840 GPU, which could offer up to a 40 percent boost in graphics performance. That’s enough to make even the most graphically demanding mobile games feel buttery smooth.
Of course, this isn't just about raw speed. The new chip also comes with an upgraded Hexagon NPU for AI tasks, promising a serious jump in on-device AI efficiency. And to keep everything connected, it’s packing the new Snapdragon X80 Modem for screaming-fast 5G, along with support for the latest Wi-Fi 7 and Bluetooth 6.0 standards.
So when can you expect to get your hands on a phone with this new silicon? Both the Xiaomi 17 series and the Samsung Galaxy S26 series are rumored to be among the first to feature the Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5, so start saving up now.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Android-to-iPhone File Sharing: Google's Quick Share Gets a Major Upgrade.
Sharing files between Android and iPhone users has long been frustrating, often requiring third-party apps, email, or a clunky workaround. Now, new details have emerged that suggest Google is about to simplify the process significantly with a major update to its Quick Share feature. A new method, currently in development, will allow seamless file transfers from Android to iOS devices using a simple QR code.
How the New QR Code System Will Work.
According to a leak found within the Google Play Services beta, the new sharing method will be a two-step process:
- Generate a QR Code: The Android user who wants to send a file will display a unique QR code on their screen.
- Scan and Download: The iPhone user will then scan this QR code to be directed to a secure, encrypted link where they can download the file directly.
This new process departs from the standard Quick Share functionality, which uses peer-to-peer technology for direct, offline transfers between Android devices. For Android-to-iPhone sharing, the files will be uploaded to Google's servers and remain available for a limited 24-hour window, which means a stable internet connection will be required for the transfer. The sender will also need to be signed into a Google account to use the feature.
 |
| Credit: Android Authority |
While a similar QR code sharing option already exists for Android-to-Android transfers when devices are offline, this new implementation is specifically designed to bridge the gap between Google's ecosystem and iOS.
A Game-Changer for Cross-Platform Sharing.
This new system is a much-needed solution to a common pain point for millions of users. It eliminates the need to rely on messaging apps that compress images and videos, or to use cumbersome services and require additional login steps. By making it easy to share high-quality files between the two largest mobile ecosystems, Google is positioning Quick Share as a powerful, cross-platform tool.
While an official launch date has not been announced, the appearance of these new features in a beta version of Google Play Services suggests a wider rollout could be coming soon.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Android 16 QPR1 Rolls Out to Pixel Devices with 'No Data Wipe' Option.
Google has begun rolling out the Android 16 QPR1 update, bringing a convenient new feature to Pixel users in the Android Beta Program. This update, which is a "No Data Wipe" over-the-air (OTA) update, allows beta testers to exit the program without having to factory reset their devices and lose all their personal data.
What This Means for Beta Testers.
Previously, users who wanted to leave the Android Beta Program after testing a feature release were required to wipe their device, which could be a significant hassle. The new "No Data Wipe" update for QPR1 (Quarterly Platform Release 1) provides a smooth and data-preserving transition. The update is less than 100 MB and also includes the September 2025 security patch.
Users can check for the update by navigating to Settings > System > Software updates > System updates. They should look for an update titled "Android Beta Exit No Data Wipe."
While the update has been spotted on some devices like the Pixel Tablet, it appears that Google is rolling it out in phases, and it may not be immediately available on all eligible devices, such as the Pixel 8a or 9a. This update is a welcome change for testers, making it much easier to transition from beta to the stable Android build.
Following the Beta 3.1 update, users who chose not to test the QPR2 Beta 1 were able to opt their devices out of the program. google.com/android/beta#devices
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Google Revives 'Androidify' with AI, Turning Selfies into Bots.
Google has relaunched its popular 'Androidify' tool, this time with powerful artificial intelligence at its core. The new app, available on the web and as a standalone Android app, allows users to transform a selfie or a text prompt into a personalized Android bot.
How It Works: The Magic Behind the Scenes.
The new Androidify app is a showcase for Google's latest AI models. When you upload a photo, it first uses Gemini 2.5 Flash to analyze the image, generating a detailed caption that describes your appearance, clothing, and accessories. This detailed description is then fed to a fine-tuned version of Imagen 3, which creates a unique Android bot that reflects your style.
Alternatively, you can skip the selfie and simply enter a text prompt to design your bot from scratch. This gives you complete creative freedom to create a custom character.
The app also serves as a demonstration for developers, highlighting how to use modern Android development practices and libraries such as Material 3 Expressive components and the ML Kit Pose Detection API.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Your Android Bot.
Creating your own Android bot is a simple and fun process. Here's how to do it:
- Open the App or Website: Download the Androidify app from the Google Play Store or visit the official Androidify website.
- Start Creating: Upload a selfie or enter a text prompt to describe your desired bot.
- Generate Your Bot: The app will use AI to generate your unique Android bot based on your input.
- Customize and Share: Once your bot is created, you can personalize it by selecting from various formats (e.g., 1:1, Wallpaper, Banner), and backgrounds.
- Animate Your Bot (Fridays Only): On Fridays in September, a limited number of users can animate their Android bot into an 8-second video using Veo 3, Google's video generation model.
You can then share your custom Android bot on social media using the hashtag #Androidify.
What Makes Androidify Stand Out?
The new Androidify experience is infinitely personal, letting you transform yourself into an Android bot in countless ways. Whether you upload a selfie or craft a fun, imaginative prompt, the AI ensures your creation feels unique and deeply customizable.
At the same time, the app is creative and fun, designed to be playful and expressive. It’s perfect for sharing with friends, showing off on social media, or simply giving your digital identity a fresh look.
For developers, Androidify is more than just a toy; it’s developer-friendly. The app has been built using the latest Android design frameworks and tools, offering a practical showcase of how modern Android UI and AI integration come together seamlessly.
And to top it off, Androidify adds a daily surprise factor. With weekly animation features powered by AI, users can see their avatars come alive, keeping the experience engaging and exciting every time they return.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Gmail for Android Gets a Fresh Look with Material 3 Expressive Redesign.
Google is rolling out a significant visual update to the Gmail for Android app, which aligns with the company's new Material 3 Expressive design language. This redesign, which has been in testing for some time, is now reaching a wider user base, offering a more modern and cohesive experience across the app.
The most noticeable change is the introduction of "expressive containers". Instead of a continuous, flat list, each email in the inbox is now placed within its own distinct card with rounded corners. This creates a cleaner, more visually separated look for each message, which some users have already started to receive. This builds on an earlier design iteration that placed the entire email list within a single, larger container.
 |
| Gmail Old Vs New |
The update also brings subtle but meaningful changes to interactions and buttons. Swipe actions for archiving, deleting, or marking an email as read now feature a "pill-shaped" animation that is both fluid and modern. When you open a message, the Reply and Forward buttons at the bottom of the screen are more prominent and leverage Dynamic Color to stand out against the background.
This Gmail redesign is part of a larger push by Google to implement the Material 3 Expressive design across its suite of applications, including Google Keep and Google Messages. The new aesthetic emphasizes rounded edges, playful motion, and vibrant color palettes to create a more engaging and user-friendly interface. While the current rollout focuses on the main inbox view and message details, certain parts of the app, such as the Compose screen and the home screen widgets, remain unchanged for now.
Also Read:
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Google Play Store Rolls Out New 'Auto-Open' Feature on New App Install.
In a move designed to improve user convenience, Google is rolling out a new "auto-open" feature for the Google Play Store. The update introduces a new toggle that allows users to automatically launch an app once its installation is complete, saving them the manual step of having to find and open the app themselves.
The new functionality appears as an "auto-open when ready" toggle located directly below the installation progress bar. By default, this option is turned off, giving users control over whether they want the app to open automatically. When a user activates the toggle, the Play Store will not only download and install the app but also launch it as soon as it's ready. To prevent accidental openings, the feature includes a 5-second countdown notification that gives users a brief window to cancel the auto-open action before the app launches.
This feature is particularly useful for apps that require immediate use after download, such as a travel app needed right before a trip or a new restaurant reservation tool. It allows users to start the download and then switch to other tasks on their device, knowing the app will be ready to use without any further interaction. While this is a clear benefit for most apps, a potential downside could be for larger applications, particularly games, where the download and installation process can be lengthy.
The new feature is reportedly rolling out widely across various Android devices, including recent models like the Galaxy Z Fold 7 and some Pixel phones. The phased rollout is a typical Google procedure, indicating that it may take time for all users to see the new option.
Also Read: Google Play Store Expands "Ask Play About This App" Feature with Gemini AI.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Google to Require Developer Verification for All Android Apps to Combat Malware.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Google Chrome Move Address Bar to Bottom in Android.
Google has introduced the feature to move the Chrome Address bar to the bottom of the screen on Android Devices. Announced in a blog post on August 3, 2025, this update enhances browsing comfort for users who prefer one-handed operation or find it easier to reach the bottom of their screens on larger devices.
The Chrome team stated, “We launched this feature because we heard your requests loud and clear. Now you can customize your browsing experience to suit your habits.” This update aligns with Google's broader efforts to offer more flexible and personalized experiences across its platforms.
Having a bigger phone screen, I will use this feature to improve control of the screen while browsing on my favourite browser. What about you? If you are using an Android phone and not using Chrome's Address Bar at the bottom, you must try it. Follow the steps given below to enable it:
How To Move the Chrome Address Bar To The Bottom?
Google has made it simple to switch the location of the address bar:
Method 1: Long-Press Option.
- Open your Google Chrome app on your Android phone.
- Long-press the address bar, and you will get options to move the address bar or to copy the link.
- Tap “Move address bar to bottom,” and you can see a smooth integration of the Address bar at the bottom of your screen.
Method 2: From Settings
- Tap the three-dot menu in Google Chrome on your Android Device.
- Go to Settings > Address Bar.
- Choose Top or Bottom according to your preference.
You can move the address bar back to the top at any time using the same methods.
If you are not able to see the above setting in your Google Chrome App, then it is the right time for you to update your Chrome Browser.
The repositioning of the address bar might seem like a small UI tweak, but it’s part of a larger design philosophy making tools more ergonomic, accessible, and tailored to user behavior. One-handed usability is becoming increasingly important as smartphone screen sizes grow.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Android’s QR Code Scanner Interface Receives Redesign.
- Android’s QR code scanner now features bottom-anchored controls and a polished launch animation for improved one-handed use.
- The redesign simplifies post-scan actions with “Copy text” and “Share” options integrated directly into the interface.
Google has quietly rolled out a refined user interface for Android’s built-in QR code scanner through a recent Play Services update. The refreshed design brings controls within thumb reach and streamlined animations, making scanning smoother and more intuitive on modern smartphones.
When users activate the QR scanner via the Quick Settings tile or on-device shortcut, they now see a brief launch animation featuring a rounded square viewfinder. Key buttons like flashlight toggle, feedback, and “Scan from photo” are consolidated into a single pill-shaped control near the bottom of the screen.
This layout contrasts sharply with the old format, where controls were placed at the top of the UI, which often made them hard to reach with one hand.
Once a QR code is detected, the scanner overlays the decoded content in a subtle scalloped circle centered on the viewfinder. The bottom panel now offers not only an “Open” option but also convenient “Copy text” and “Share” actions, eliminating the need to navigate away from the scanning screen.
This design refresh improves usability in real-world scenarios where users often scan QR codes with one hand while multitasking. By repositioning interaction points lower on the screen, the interface reduces strain and increases accessibility.
The new layout also adds functionality by including quick-choice options right after scanning. Whether opening the link, copying content, or sharing the result, users can act faster without leaving the app.
Although Google originally previewed this redesign in its May 2025 release notes for Play Services version 25.19, the visual overhaul is only now becoming widely available as part of the v25.26.35 rollout. Since the update is delivered via Google Play Services, users may need to restart their device or wait a few hours for it to appear even if they are on the latest build.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Google Adds AI Mode Shortcut to Android Search Widget.
- Android users can now launch AI Mode from the Search widget with a dedicated shortcut, boosting access to Gemini-powered search.
- The customizable widget shortcut is rolling out with Google app 16.28 and enhances usability without needing Search Labs enrollment.
Google is now rolling out a convenient shortcut to AI Mode directly on the Android Search widget, giving users one-tap access to its AI-powered search interface. The AI Mode icon appears in its own circle next to the voice and Lens shortcuts, making it quick to launch full-screen Gemini‑powered search responses.
What’s New in Google AI Mode and How to Use It.
Starting with app version 16.28, both beta and stable users can now customize the Google Search widget to include the AI Mode button. Long-pressing the widget brings up a Customize menu where you can enable AI Mode under Shortcuts. It will then appear alongside existing icons for voice search and Lens.
Here is a step-by-step process of how to enable Google AI Mode:
Step 1: Open the Google Search App on your Android phone.
Step 2: Click on your profile in the top-right corner and go to Settings.
Step 3: Select Customise Search widget and then select Shortcuts.
Step 4: Inside Shortcuts, you will get an option to add AI Mode to your Google Search.
When you tap the AI Mode shortcut, it launches a full-screen interface where you can enter any prompt and receive AI-generated responses. It functions like a conversational search tool, using Gemini’s query fan-out technique to break down your question into subtopics and provide comprehensive information.
Users not enrolled in Search Labs may see the older Locate AI interface, where AI Mode is available in a pill-style button within the Discover feed instead of the widget area. Google encourages users to join Search Labs for a cleaner and more integrated experience.
Also Read: Google Launches AI-Powered Web Guide to Organize Search Results.
How Google AI Mode is Useful for the User.
The widget shortcut makes AI Mode more accessible and intuitive. It removes the need to open the Google app first and streamlines access for users who want next-generation search directly from their home screen.
This update reflects Google’s broader push to integrate AI deeply across its products. While new AI tools like Deep Search and Gemini 2.5 Pro are reserved for subscribers, the widget shortcut brings AI Mode to more casual users in a familiar format.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Android Introduces “Expanded Dark Mode” to Force a Dark Theme
Google is testing a powerful accessibility-focused feature in the second Android Canary build that forces Dark Mode on apps without native dark themes. Dubbed Expanded Dark Mode, it sits alongside the traditional “Standard” dark theme and brings remarkably better system-wide consistency—though not without caveats.
What’s new in Expanded Dark Mode?
Standard Dark Mode: Applies a dark theme only to Android system UI and apps that support it natively.
Expanded Dark Mode: Extends dark styling to apps that lack built-in dark themes. It works more intelligently than the previous “override force‑dark” option, avoiding blanket color inversion in favor of a more refined approach.
Because this feature is experimental and only available in Canary builds, users may encounter visual glitches in some apps—such as inconsistent colors or layout issues. Google openly cautions users that not all apps will “play nice,” and in such cases recommends switching back to Standard mode .
The rollout timeline for Beta or Stable channels is not confirmed, though speculation places it in Android 16 QPR2 (expected December 2025).
How to Enable Expanded Dark Mode (In Android Canary builds)
If you’re using an Android device enrolled in the Canary channel, here’s how to turn it on:
Step 1. Open Settings.
Step 2. Navigate to Display & touch → Dark theme.
Step 3. You’ll now see two modes:
- Standard
- Expanded
 |
| Credit: Android Authority |
Step 4. Select Expanded to enforce dark styling across more apps—even ones without native support.
Step 5. If you notice any display or layout glitches in specific apps, toggle back to Standard mode.
This feature replaces the older hidden “make more apps dark” or “override force‑dark” settings found in Developer Options, offering a cleaner, user-facing placement in the display settings.
How This Update Will Be Useful?
Users who read or browse their phone in low-light environments—such as at night—will find a more consistent, eye-friendly experience even with apps that haven’t been optimized for dark mode.
While Developer Options offered “override force-dark,” Expanded Dark Mode appears to use more intelligent logic to convert UI elements without distorting images or causing widespread visual distortion.
This feature is part of an unstable release. You should expect bugs. Android will let you revert to Standard mode if that improves app stability or appearance .
When it arrives in Beta or Stable under Android 16 QPR2 or later, it could become a key feature for dark‑mode enthusiasts.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
How the Android Earthquake Alerts System Works?
Why Early Earthquake Warning Is Important
Data Sources: Seismic Networks and Crowdsourced Accelerometers
Seismic Networks
Crowdsourced Accelerometers from Android Devices
The ShakeAlert® Partnership
Crowdsourced Detection via Android Phones
- P‑waves: Fast-arriving, less intense—detected first.
- S‑waves: Slower but more destructive.
Alert Generation.
- Be Aware: Signals light shaking; non-intrusive notifications guide readiness.
- Take Action: Signals moderate to strong shaking; these alerts override the phone screen with a loud alarm and safety instructions.
Quick FAQ.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
Everything New in Android 16 QPR1 Beta 3.
Android 16 QPR1 Beta 3 (build BP31.250610.004) has landed, and it's shaping up to be the final polishing step before the stable release expected in September. If you're enrolled in the QPR1 beta on compatible Pixel devices, you’re getting a refined experience with essential bug fixes, minor UI upgrades, and two standout features designed for accessibility and productivity. Let’s explore what's new.
Android's Quarterly Platform Releases (QPR) deliver regular, bug-focused improvements to the OS without introducing major new APIs ideal for stability and polish. Beta 3 marks the last preview of QPR1, heavily focused on enhancing reliability before the stable rollout.
Key Features & UI Enhancements.
Keyboard Magnifier in Accessibility
One of the most meaningful additions in Android 16 QPR1 Beta 3 is the Keyboard Magnifier, specifically designed for users with low vision. Found under Settings → Accessibility → Magnification, this new toggle allows users to magnify just the keyboard when it's active, without zooming the entire screen.
This seemingly small change has huge implications for accessibility. Previously, magnifying a screen meant zooming in on all UI elements, which could be disorienting and slow. With the Keyboard Magnifier, the rest of the screen remains static while just the keyboard is enlarged, letting users comfortably type messages, search queries, or login credentials with less visual strain.
Desktop Mode Shortcut Enhancements.
5-Bar Cellular Signal UI.
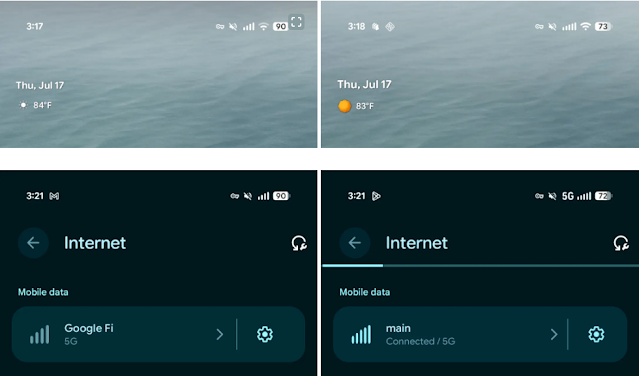 |
| Credit: 9to5Google |
Refined Settings & System UI Details
- Spacing between settings options has been slightly adjusted for better tap targets and visual clarity.
- Toggle switches now have a more responsive animation, creating a smoother feel during navigation.
- The At-a-Glance widget on the home screen has been restored to include colorful weather icons, improving both the aesthetic and usability at a glance.
Nine Major Bug Fixes.
This Beta addresses nine headline issues flagged by users:
-
RTOS task list kernel bug causing restarts
-
Launcher display glitches
-
Notification rendering problems
-
Media player malfunction in shade
-
Class loader restart bug
-
Kernel-caused restarts
-
Camera startup black screen fix
-
Status bar padding adjustments
-
Notification folding issues.
With at least nine key problems resolved, the update significantly boosts device reliability.
What's Still Missing?
Several experimental improvements remain absent from Beta 3, including:
-
Qi2 charger screen savers
-
Enhanced HDR brightness toggle
-
Dedicated "Parental controls" menu
-
New 90:10 split-screen ratio
-
Tablet bubble bar and lock‑screen blur UI.
Google appears to reserve these for future Canary or stable builds.
This release supports Pixel 6 and newer, including Pixel 6a, 7/7 Pro, 7a, Fold, 8 series, 9 series, and Pixel Tablet. If you're enrolled in QPR1 beta and want stability over bleeding-edge features, this is an optimal moment to either remain enrolled or opt out ahead of the September stable release.
Google expects to launch Android 16 QPR1 Stable on September 3, 2025. To ensure you receive it, unenroll post-Beta 3—you’ll otherwise be moved to QPR2.
 I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.
I'm a full-time Software Developer with over 4 years of experience working at one of the world’s largest MNCs. Alongside my professional role, I run a news blog, WorkWithG.com, which focuses on Google tools, tutorials, and news. I'm passionate about breaking down complex topics and making learning accessible for everyone.



.png)


































 Latest Google News, Updates, and Features. Everything You Need to Know About Google
Latest Google News, Updates, and Features. Everything You Need to Know About Google